Paper Reading: "wPerf: Generic Off-CPU Analysis to Identify Bottleneck Waiting Events"
One Line Summary
Some waiting events can cast impact to multiple threads. A method which can computes not only the local impact of a waiting event, but also whether such impact can indirectly reach other threads is developed.
Important terms
- On-CPU analysis: Used to identify bottlenecks created by execution.
- Off-CPU analysis: Used to identify bottlenecks created by waiting.
- False wakeup: A phenomenon that a thread is woken up but finds its condi- tion to continue is not satisfied, so it has to sleep again.
- Knot(in the wait-for graph): A section which never wait for the outside threads. Because optimizing outside events will not influence the status inside(and will not improve overall thoughput), so each knot must contain a bottlenect. In a graph, a knot is a nonempty set K of vertices such that the reachable set of each vertex in K is exactly set K; a sink is a vertex with no edges directed from it.
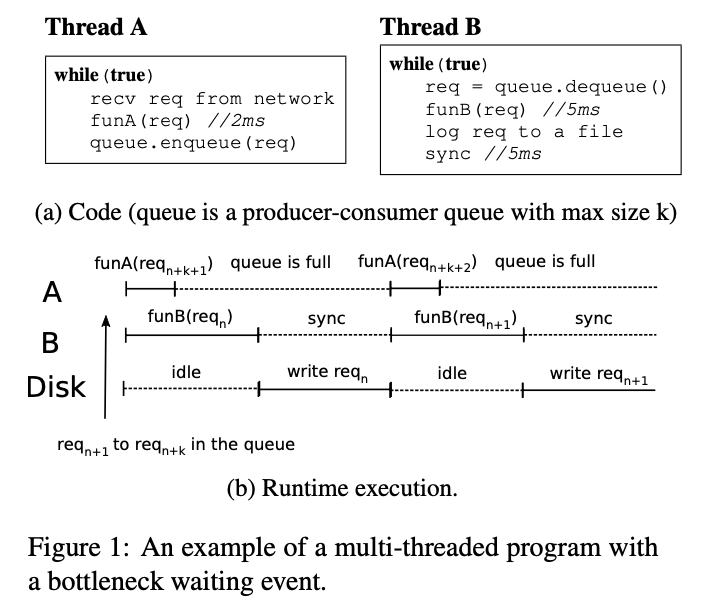
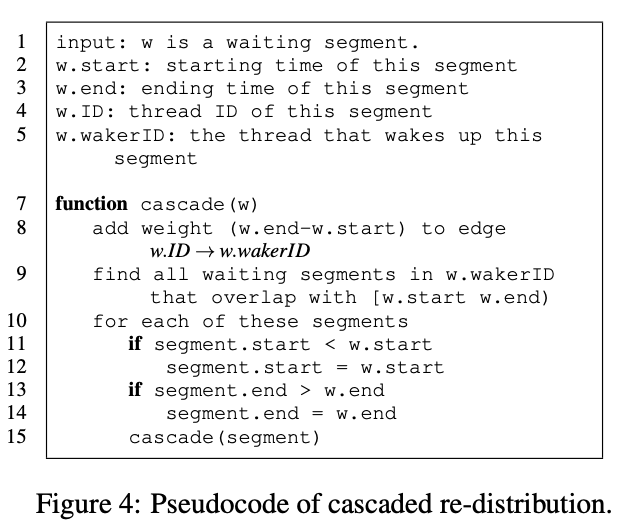
- Cascaded redistribution: If thread A waits for thread B from t1 to t2, wPerf checks what B is doing during t1 to t2 and if B is waiting for an- other thread, wPerf will re-distribute the corresponding weight and perform the check recursively.
Points
- wPerf act on events(Get the impact of events on all threads).
- On-CPU analysis already has some tools good enough, while Off-CPU analysis is still inaccurate.
- Wait-for graph: Each thread is a vertex and a directed edge from A to B means the time thread A waits for B.
- Events with a small local impact usually have a small global im- pact, but events with a large local impact may not have a large global impact.
- Things to be recorded: scheduling events, IRQ(interrupt request) events, information for I/O devices, information for busy waiting, call stacks.
- wPerf can start and stop recording at any time.
- wPerf treat I/O device as a pseudo I/O thread.
- In order to minimize the overhead, recorder buffers events and flushs the buffers to trace file in the background. Also, the recorder creates a buffer and a trace file for each core to avoid contention.

Graphs
Pros
- It innovatively utilizes the “wait-for” graph method to investigate the wating relationship between threads, which make it easy to locate the bottleneck.
- wPerf takes all these I/O operation, busy waiting, false wakeup into consideration, which make it more accuarte and competible to various cases.
- Introduced “cascaded redistribution” which can help us find the origin bottleneck rather than simply take the waiting thread as the reason of latency.
Cons
- It can not be applied to distributed system currently.
- It mainly foucuses on Off-CPU analysis, it may consider the combination of both On-CPU and Off-CPU analysis.
- It brings in overheads in its recording process, especially when there are many waiting events.
Zhongyang Zhang